Introduction to BIM community guidance
The BIM Community.org guidance and protocols are designed to enable a lifecycle approach to using BIM as information management and inherent the requirements, vision and implementation requirements originally identified within the UK BIM Level 2 suite of documentation. The purpose of these guidance and protocols is to establish a working implementation of BIM as ISO 19650 that achieves the reduction in waste and increases to productivity required to improve the way we design, build, operate and maintain buildings and their assets.
The BIM Community.org guidance and protocols are designed to specify, manage, and assess BIM deliverables by architects, engineers, surveyors, and constructors globally. The use of the BIM Community.org guidance and protocols should ensure that project deliverables produced using the BIM processes achieve an agreed level of quality.
The principle of the development of the BIM Community.org guidance and protocols are that the planning, implementation, management and checking of the use of BIM on a project requires client direction, involvement, and leadership along with design consultant and constructor collaboration.
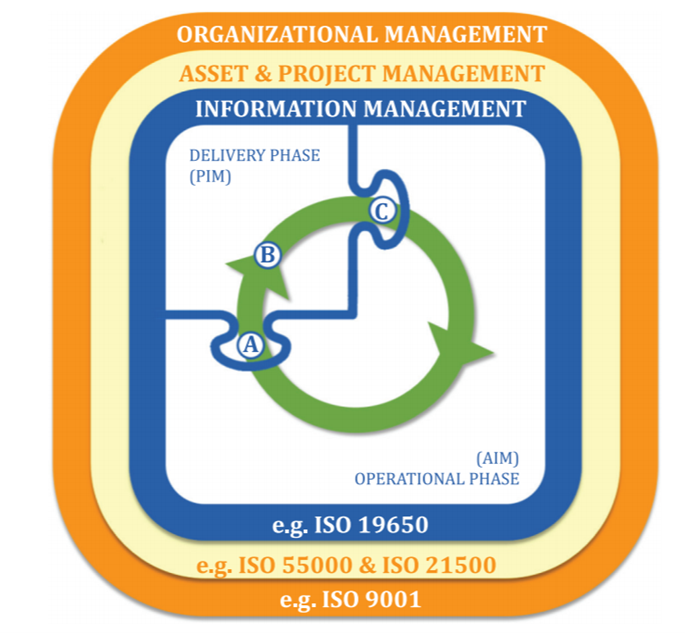
Figure 1 ISO 19650-1:2018(E)
Key
- A start of the delivery phase – transfer of relevant information from Asset Information Model (AIM) to Project Information Model (PIM)
- B progress development of the design intent model into the virtual construction model
- C end of the delivery phase – transfer of relevant information from PIM to AIM
BIM as Building Information Management is the process of generating and managing information during the planning, design, construction, operation and maintenance stages of a building or an asset throughout its life cycle. Typically, the process uses three-dimensional modelling software(s) to increase the productivity of consultants and constructors during design and construction. All the information collected / generated during these stages can then be made available to be utilized by the operation stage.
The process produces Building Information Model(s), which encompasses geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, quantities, properties, and other assigned properties or attributes of elements. Building information models can be utilized by different stakeholders at different stages for different purposes. However, these purposes must be identified early in the process as the method and associated cost of delivery is dependent upon the purposes.
The BIM Community.org guidance and protocols establish a process for adopting BIM on building and infrastructure projects. Clients, project managers, architects, engineers, surveyors, constructors, manufacturers, and facility managers can reference this standard to understand their role and responsibilities on a project.
Every project, whether this defines just a specific stage (i.e. Design) or the entire life cycle of a facility that adopts BIM, shall have a clearly defined outcome from the BIM process. The purpose of the BIM process should be set out and agreed by the Client with the design consultants and Constructor at the beginning of a project or project stage.
The successful delivery of the BIM process to meet the established targets then requires careful planning, detailed BIM specifications, and a defined set of procedures and methodologies for the implementation of the BIM process.
The production of the models shall be carried out by architects, engineers, surveyors, specialist designers, and constructors with appropriate software applications and at different times during the phases of the project. The client should appoint a professional BIM or information manager to lead and support the BIM process. The BIM or information manager could be an architect, engineer, surveyor, constructor or an independent BIM professional with relevant practical construction knowledge and design coordination experience.